Excessive Invariance Causes Adversarial Vulnerability
Jacobsen et al., 2019
 Source: Jacobsen et al., 2019
Source: Jacobsen et al., 2019Summary
- Adversarial vulnerability in DNNs results from both sensitivity to task-irrelevant changes, as well as insensitivity to task-relevant changes
- Class-specific content can be manipulated without changing the hidden activations
- Identitfy standard cross-entropy loss as a reason and propose extension to the objective to encourage consideration of all task-relevant features
- Links: [ website ] [ pdf ]
Background
- Adversarial examples demonstrate that while DNNs may demonstrate super-human performance on many tasks, tiny shifts to the input can cause them to make unintuitive mistakes
- Excessive invariance that causes adversarial vulnerability is likely a result of classifiers that rely only on a few highly predictive features
- Cross-entropy maximizes a bound on the mutual information between labels and representations, without incentivizing explaining all class-dependent variables
Methods
- Complementary views of adversarial examples
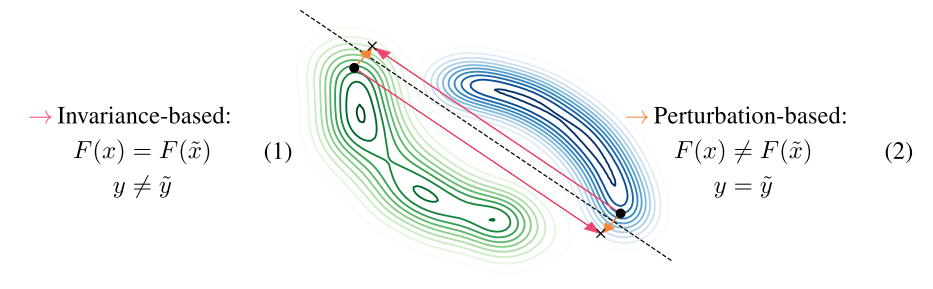
- Perturbation-based: model produces a different output to the adversarial example, but the ground-truth (oracle) label is the same (nuisance perturbation)
- Invariance-based: model produces the same output to the adversarial example, but the ground-truth (oracle) label is different (semantic perturbation)
- Use fully invertible RevNet (bijective classifier) where first
- Achieves comparable performance to popular CNNs (VGG19, ResNet-18)
- Create adversarial examples with metameric sampling:
- Three ways to increase mutual information between label and bijective network representation
- Directly increase
- Indirectly increase
- Reduce
- Directly increase
- Independence cross-entropy loss for bijective networks adds term to minimize unused information
Results
- Applying metameric sampling to fully invertible RevNet trained on MNIST and ImageNet shows that the nuisance variables dominate the visual appearance
- Same results when using feature adversaries on ResNet-152
- Using independence cross-entropy loss reduces invariance-based vulnerability compared to standard cross-entropy
- Results on shiftMNIST, where highly predictive features are introduced for training but removed in testing, shows a significant (but not total) reduction in error rate
Conclusion
- The use of bijective networks to identify large subspaces of invariance-based vulnerability is interesting
- While the proposed independence cross-entropy loss had promising results, it is only applicable to bijective networks